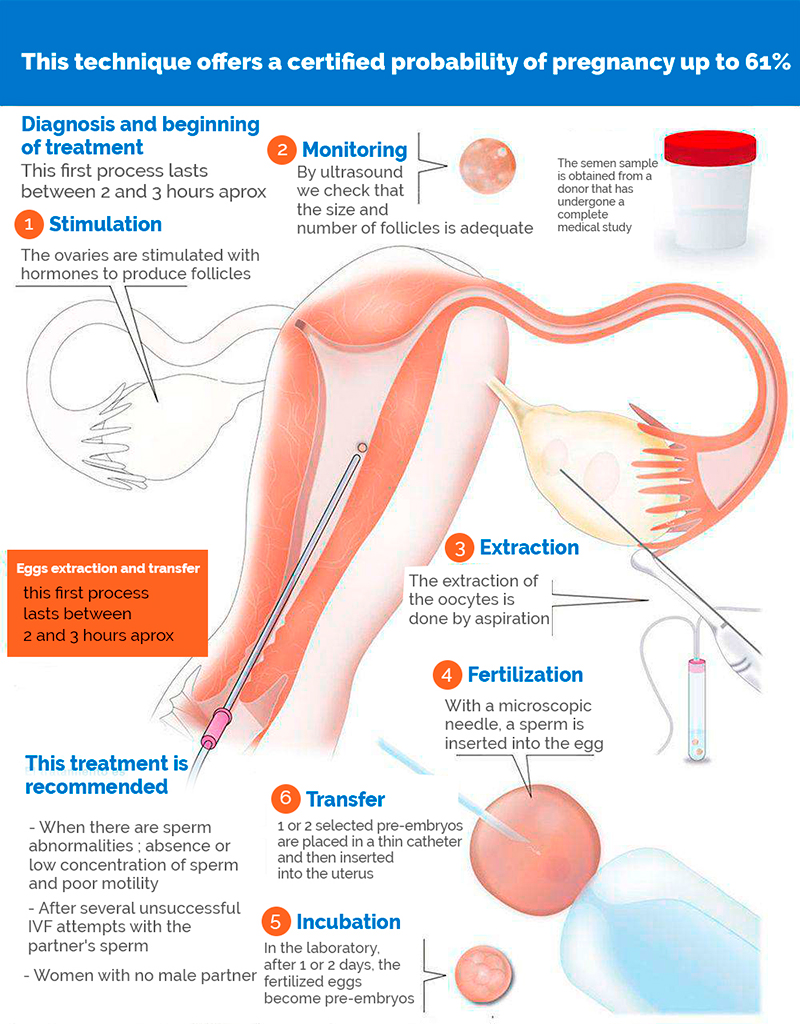
In Vitro fertilization with your own eggs and donor semen is a laboratory technique that fertilize the previously extracted eggs with the sperm of an anonymous donor. The donor sample has optimal conditions of quality and quantity, since it comes from a healthy donor. Once fertilized, the egg becomes a pre-embryo and it's transferred to the uterus for further development. This technique offers a certified probability of pregnancy up to 61%.
In which cases is this recommended?
This type of IVF is used when you want to be a single mother, your partner is another woman or after several unsuccessful IVF attempts with the partner's semen and in which we suspect that the origin of the failures may be from the male partner. It is also used in cases of azoospermia (medical condition of a man whose semen contains no sperm) or when the semen has been used without success. Or, more rarely, when the man has a chromosomal abnormality and, for ethical reasons, it is not contemplated to undergo the preimplantation genetic diagnosis (study of the chromosomal characteristics of the embryo before being implanted in the uterus).
IVF STEPS
1. Monitoring and ovaries stimulation
The ovaries are stimulated through the administration of hormones (FSH-stimulating follicle and, in some cases, LH luteostimulatory). The development of the cycle is monitored by ultrasound until it is verified that the number and size of the follicles is adequate. Then, another hormone that simulates LH is administered, which is the hormone that naturally causes ovulation, allowing the release of the egg..
2. Obtaining the sperms sample
The semen sample is obtained from a donor that has undergone a complete medical study (semen analysis, blood and urine tests, general examination, study of sexually transmitted diseases and psychological examination) to ensure the quality of his sperm and rule out any pathology. All donors are of legal age and sign a consent and anonymity of their donation. The semen is frozen before use and remains unused for a minimum of 6 months to guarantee the window period of certain sexually transmitted diseases.
3. Eggs extraction and In Vitro Fertilization
The extraction of the oocytes is done by puncture and aspiration of the follicles. It is a procedure that requires anesthesia(sedation). Once retrieved, the eggs are kept for a few hours in culture environment, and, in the meantime, the semen is prepared to isolate the motile sperm. If the technique to be used is ICSI (microinjection of one sperm into each mature egg), the eggs are denuded, which means that the cells surrounding their surface are removed, and one sperm is injected into each of them. In our center we perform ICSI in 99% of cases, and we don't do otherwise unless a different process is indicated. In the case of performing a classic In Vitro Fertilization, the sperms (between 50,000 and 100,000) are placed in the culture environment where the eggs are, and the next day, we check how many of them have been fertilized.
En el caso de practicar una fecundación in vitro clásica, se colocan los espermatozoides (entre 50.000 y 100.000) en el medio del cultivo donde están los óvulos y al día siguiente se comprueba cuántos de ellos han sido fecundados. Obviamente, cuanto mayor es el número de óvulos y mejor calidad tenga el semen mayores son las posibilidades de obtener embriones. Esta técnica tiene el inconveniente de ofrecer menores tasas de fertilización, dado que el espermatozoide no es introducido directamente en el óvulo.
4. Transfer
Only on the day after the eggs extraction and the ICSI(Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) we will know the number of the fertilized ones. Over the next 2-3 days these fertilized eggs develop into pre-embryos ready to be transferred to the uterus. On the day of the transfer, the pre-embryos with the best development characteristics are selected. According to the law, we can transfer up to 3 pre-embryos but the most common average number is 2. The pre-embryos are inserted into a fine catheter and are channeled by the gynecologist to the end of the uterus(anesthesia is not necessary). Of the transferred pre-embryos, usually only one of them is implanted, but sometimes more than one gets there, which would lead to a multiple pregnancy.
5. Cryopreservation
The non-transferred pre-embryos are frozen using liquid nitrogen (this cryopreservation is known as vitrification) and are subsequently stored in an embryo bank appropriately identified. These pre-embryos can be used in subsequent cycles if pregnancy is not achieved on the first attempt. Obviously, the treatment to prepare the uterus for a frozen embryo transfer is much easier since the stimulation and extraction of oocytes is not necessary.
SUCCESS RATE
IREGA CANCÚN
- Hospital Galenia Planta Baja Av. Tulum Lote 01 Maza. 01 SM 12 Fracc. Sta. Maria Sike Esq. Nizuc, C.P. 77505